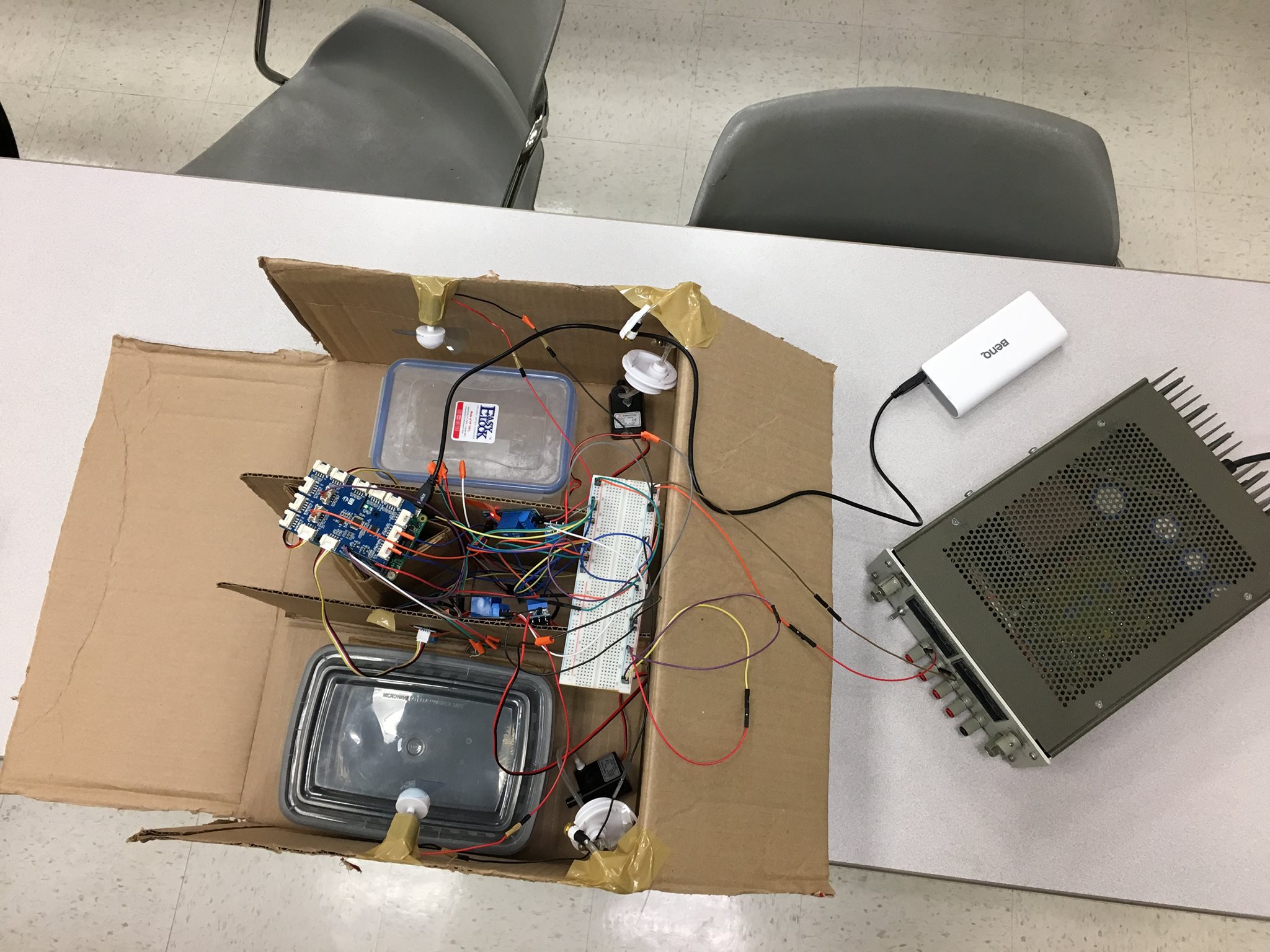

Complete Model Setup
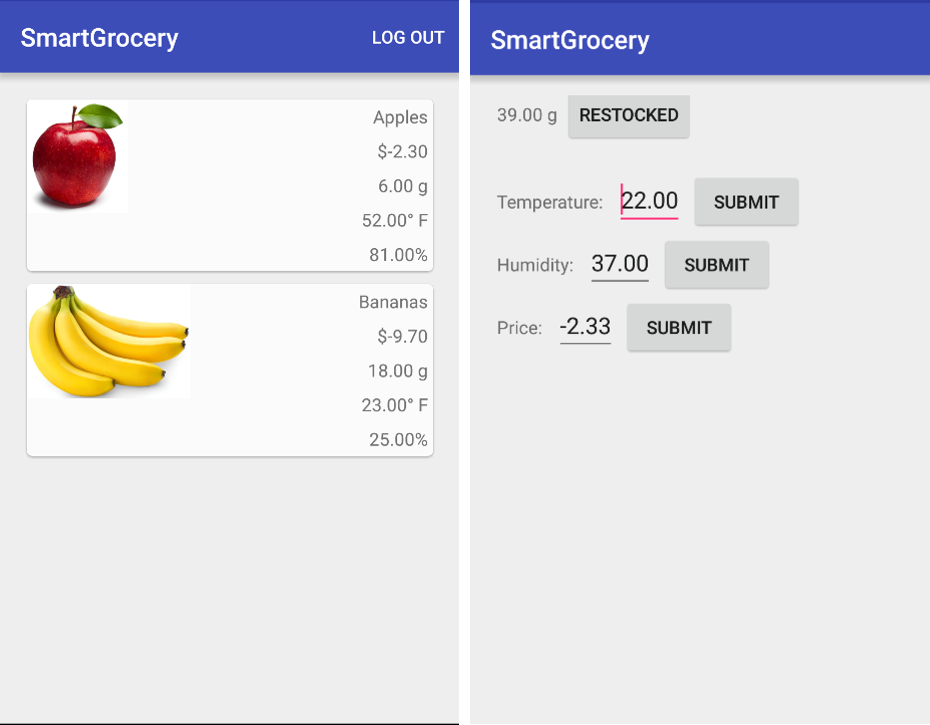
Columbia University
EECS E4764 Fall'16 Internet of Things
Intelligent and Connected Systems
Team 5 Project
Report

© Google Images
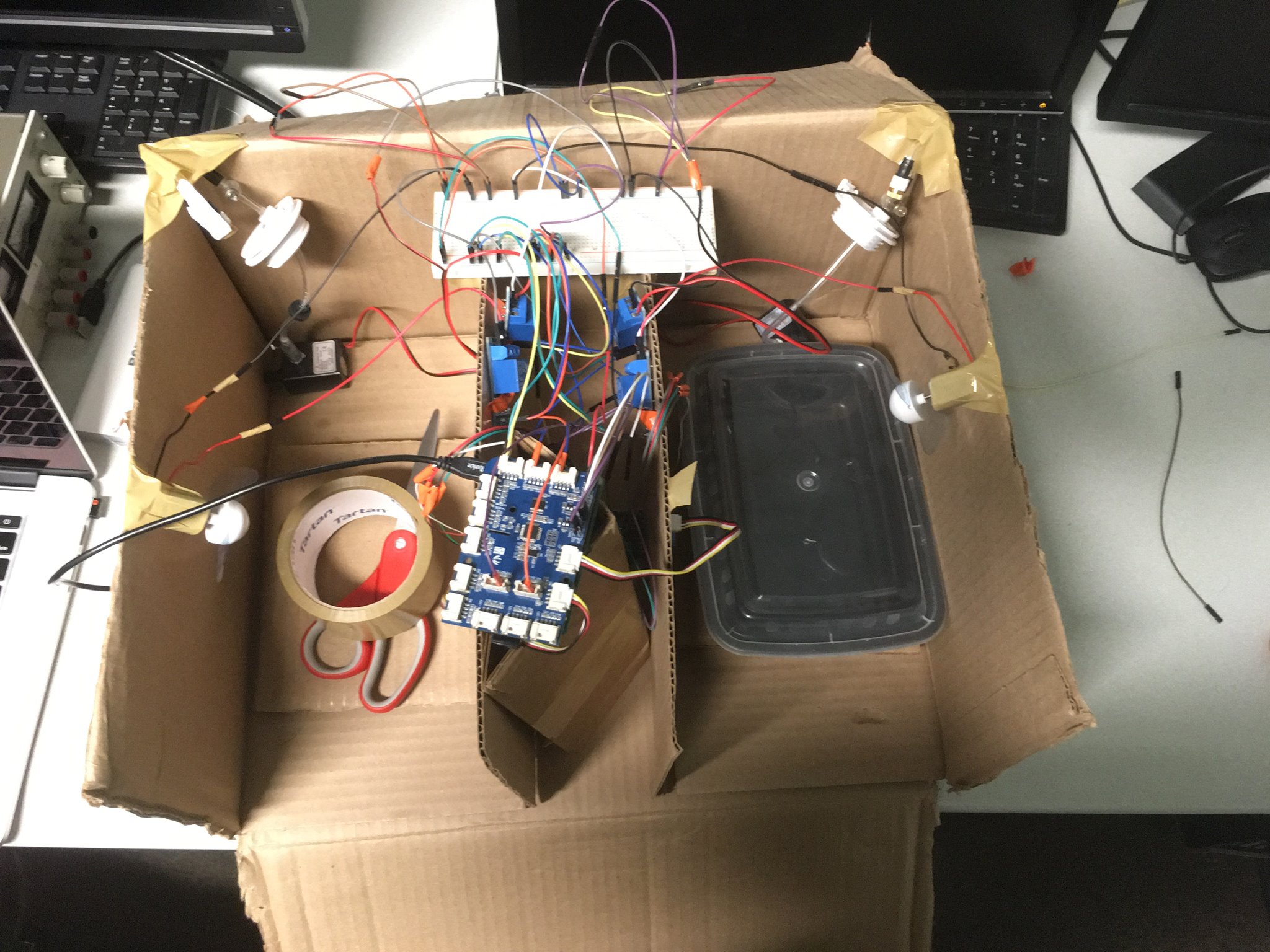
The various components deployed here are:

Contact Name 1: Florian Shabanaj, email: fs2564@columbia.edu
Contact Name 2: Ming Zhou, email: mz2591@columbia.edu
Contact Name 3: Rahul Rana, email: rr3087@columbia.edu
Columbia University Department of Electrical Engineering
Class Website:
Columbia University EECS E4764 Fall '16 IoT
Instructor: Professsor Xiaofan (Fred) Jiang